Application 是如何被创建和初始化的?
时序图
从 startActivity 开始,比如打开一个 app 的首页,当 app 未启动时就会走创建 Application 这条路
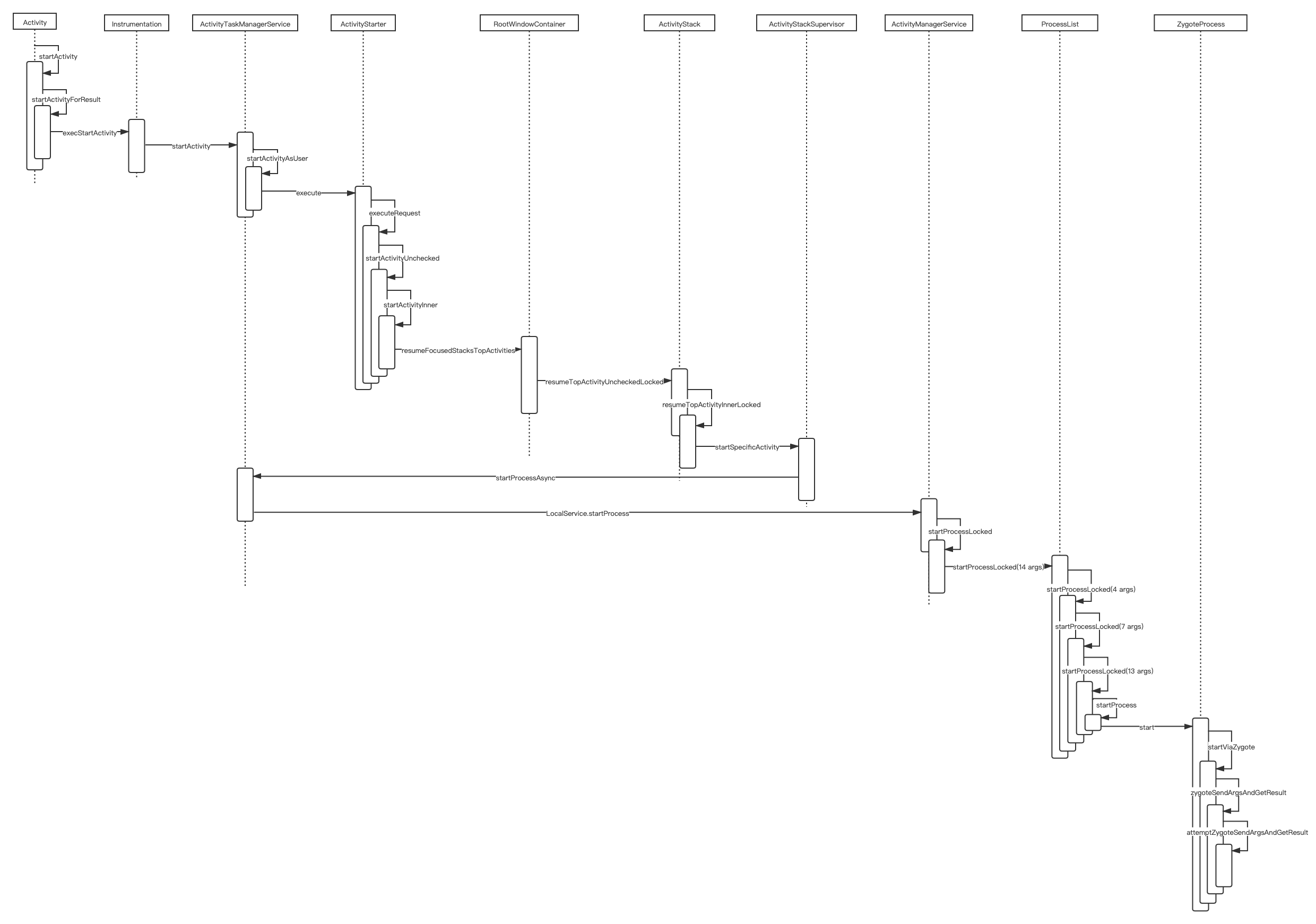
AMS 承担的工作
其中的转折点在 resumeTopActivityInnerLocked,发现 app process 不存在,走启动 app process 的流程
private boolean ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
// ... Launching this app's activity, make sure the app is no longer considered stopped. 下面是启动 Activity 的逻辑
if (next.attachedToProcess()) {
// ...
} else {
// 此时 app process 还没有起来,走下面一段逻辑
// Whoops, need to restart this activity!
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
next.showStartingWindow(null /* prev */, false /* newTask */, false /* taskSwich */);
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Restarting: " + next);
}
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Restarting " + next);
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivity(next, true, true);
}
}最后走到 attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult,AMS 将 app 的相关参数通过 socket 发送给 zygote 进程,由 zygote 负责 fork 出一个 app process,这一段路程就算完结了
private Process.ProcessStartResult attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(ZygoteState zygoteState, String msgStr) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
final BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = zygoteState.mZygoteOutputWriter;
final DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = zygoteState.mZygoteInputStream;
zygoteWriter.write(msgStr);
zygoteWriter.flush();
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = zygoteInputStream.readInt();
result.usingWrapper = zygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with Zygote - " + ex.toString());
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}值得注意的是,AMS 是通过 LocalSocket 与 zygote 交互的,它们建立连接的过程如下:
private Process.ProcessStartResult ZygoteProcess.startViaZygote(...) {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<>();
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
// 拼接字符串参数 ...
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), zygotePolicyFlags, argsForZygote);
}
private ZygoteState ZygoteProcess.openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
attemptConnectionToPrimaryZygote();
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
if (mZygoteSecondarySocketAddress != null) {
attemptConnectionToSecondaryZygote();
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to zygote", ioe);
}
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}
private void ZygoteProcess.attemptConnectionToPrimaryZygote() throws IOException {
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mZygoteSocketAddress, mUsapPoolSocketAddress);
maybeSetApiDenylistExemptions(primaryZygoteState, false);
maybeSetHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(primaryZygoteState);
}
}
static ZygoteState ZygoteState.connect(LocalSocketAddress zygoteSocketAddress, LocalSocketAddress usapSocketAddress) throws IOException {
DataInputStream zygoteInputStream;
BufferedWriter zygoteOutputWriter;
final LocalSocket zygoteSessionSocket = new LocalSocket()
if (zygoteSocketAddress == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("zygoteSocketAddress can't be null");
}
try {
zygoteSessionSocket.connect(zygoteSocketAddress);
zygoteInputStream = new DataInputStream(zygoteSessionSocket.getInputStream());
zygoteOutputWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(zygoteSessionSocket.getOutputStream()), Zygote.SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE);
} catch (IOException ex) {
try {
zygoteSessionSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ignore) {}
throw ex;
}
return new ZygoteState(zygoteSocketAddress, usapSocketAddress, zygoteSessionSocket, zygoteInputStream, zygoteOutputWriter,
getAbiList(zygoteOutputWriter, zygoteInputStream));
}走入 zygote
从 zygote 开始
下面就轮到 zygote 出场了,zygote 进程是 system server 和 app 进程的父进程,它在 java 的入口点是 ZygoteInit.main;zygote 启动后会加载各个进程共享的资源,然后启动 system server,最后工作在主循环 runSelectLoop 上;在 runSelectLoop 里,zygote 通过 epoll 监听 zygote server socket 并根据请求参数 fork 出 app 进程(上面也说到过 AMS 是通过 LocalSocket 请求让 zygote fork app process)
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
/**
* zygote 的入口点
* This is the entry point for a Zygote process. It creates the Zygote server, loads resources,
* and handles other tasks related to preparing the process for forking into applications.
*/
public static void ZygoteInit.main(String[] argv) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
// ...
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
// ...
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
// ...
}zygote server socket 实际上是个挂载在 /dev/sockets/ 目录下的 FD,它是由脚本 init.rc 创建的,这个 FD 可以通过环境变量 ANDROID_SOCKET_<socketName> 获得
ZygoteServer(boolean isPrimaryZygote) {
mUsapPoolEventFD = Zygote.getUsapPoolEventFD();
if (isPrimaryZygote) {
mZygoteSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME); // PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME = "zygote"
mUsapPoolSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.USAP_POOL_PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
} else {
mZygoteSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME);
mUsapPoolSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.USAP_POOL_SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME);
}
mUsapPoolSupported = true;
fetchUsapPoolPolicyProps();
}
/**
* Creates a managed LocalServerSocket object using a file descriptor
* created by an init.rc script. The init scripts that specify the
* sockets name can be found in system/core/rootdir. The socket is bound
* to the file system in the /dev/sockets/ directory, and the file
* descriptor is shared via the ANDROID_SOCKET_<socketName> environment
* variable.
*/
static LocalServerSocket Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(String socketName) {
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName; // ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX = "ANDROID_SOCKET_"
try {
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Socket unset or invalid: " + fullSocketName, ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
return new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error building socket from file descriptor: " + fileDesc, ex);
}
}而 zygote 主循环的整个代码就是 epoll 多路复用的模型
/**
* Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
* worth at a time.
*/
Runnable ZygoteServer.runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
// ...
while (true) {
// epoll 可以同时监听多个 FD:pollFDs,当 epoll 返回时要逐个处理
StructPollfd[] pollFDs;
pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size()];
int pollIndex = 0;
for (FileDescriptor socketFD : socketFDs) {
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = socketFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
// ... 阻塞直到 pollFDs 里有消息输入
int pollReturnValue;
try {
pollReturnValue = Os.poll(pollFDs, pollTimeoutMs);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
// ... 第一个 PD 总是 Zygote server socket,它接收 fork 请求并创建一个新的 FD 与对方交互
while (--pollIndex >= 0) {
if (pollIndex == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
socketFDs.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
} else if (pollIndex < usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
// 从 FD 里解析请求参数并处理
ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(pollIndex);
boolean multipleForksOK = !isUsapPoolEnabled() && ZygoteHooks.indefiniteThreadSuspensionOK();
final Runnable command = connection.processCommand(this, multipleForksOK); // commands alaways null in zygote server
// ...
}
}
}
}fork app process
下面看看 zygote 是怎么 fork 出 app process 的
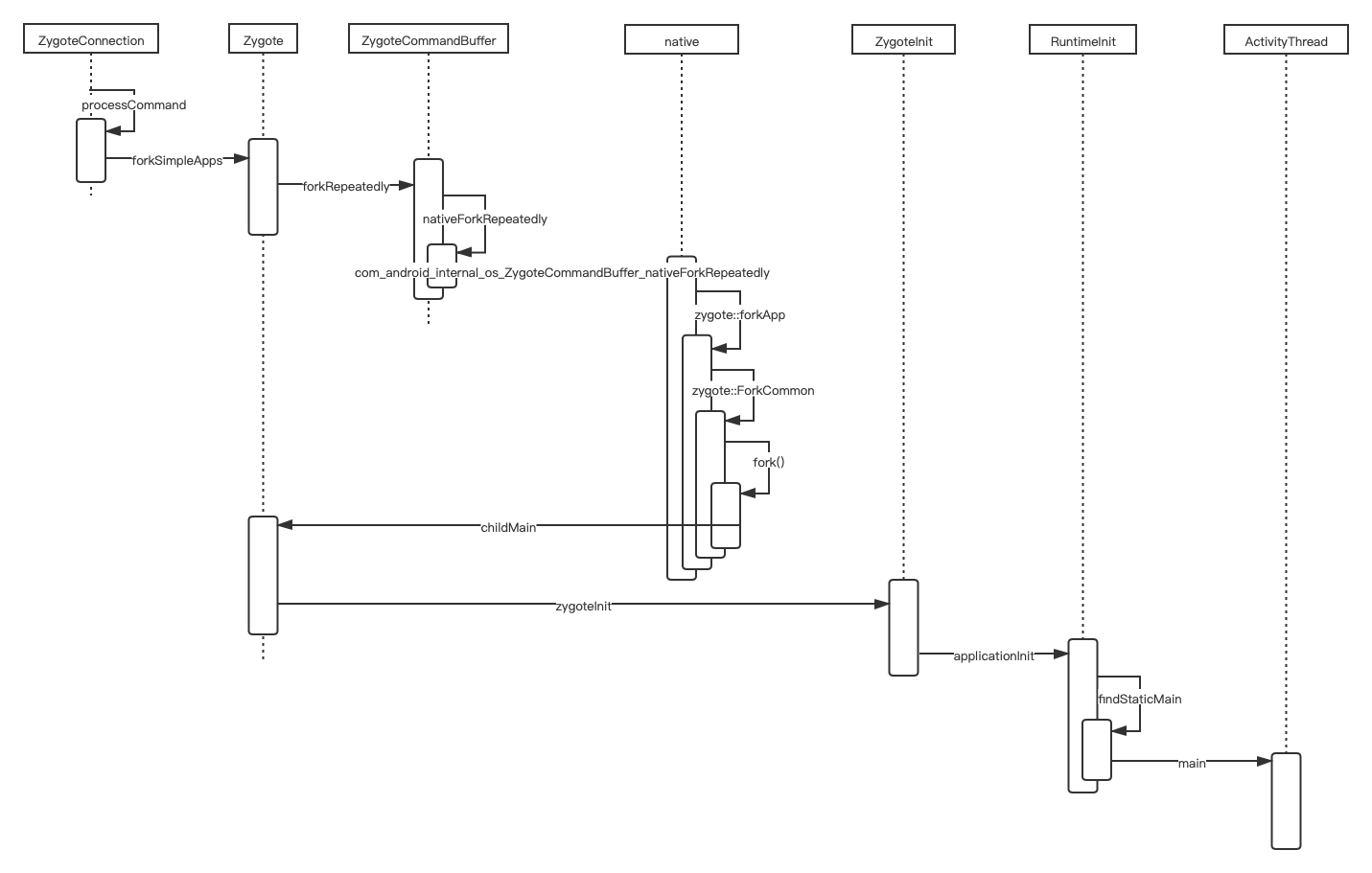
在 fork() 系统调用后,返回 0 表示当前处于子进程,> 0 处于父进程(也就是 zygote)
zygote 进程会继续它的主循环 runSelectLoop,而子进程会跳出主循环,执行 ZygoteConnection.processCommand 返回的 Runnable
public static void ZygoteInit.main(String[] argv) {
// ...
Runnable caller;
try {
// ...
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} ...
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}这个 Runnable 实际上是通过反射调用 ActivityThread.main
// app 进程的 entry point 被设置为 android.app.ActivityThread
boolean startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, HostingRecord hostingRecord,
int zygotePolicyFlags, boolean disableHiddenApiChecks, boolean disableTestApiChecks,
boolean mountExtStorageFull, String abiOverride) {
// ...
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
final String entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
return startProcessLocked(hostingRecord, entryPoint, app, uid, gids, runtimeFlags,
zygotePolicyFlags, mountExternal, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith, startTime);
}
// 寻找方法 main(String[] args)
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing class when invoking static main " + className, ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException("Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
// 通过反射调用 main 方法
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}Application 实例的创建和初始化
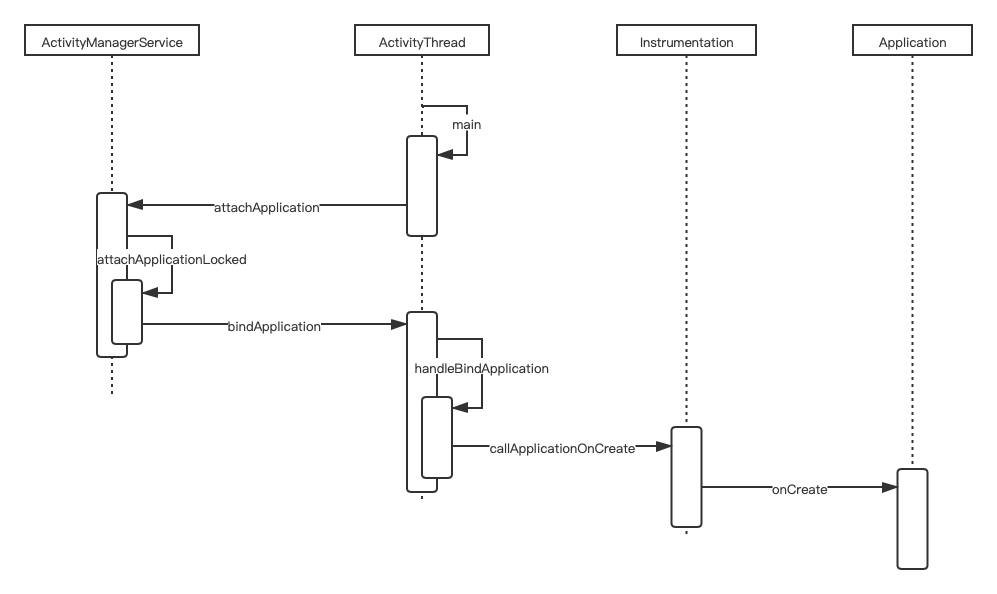
app process 的起始点是 ActivityThread.main,做完所有准备龚州工作后进入 loop 循环,后续的任务通过 Handler 执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// ...
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}ActivityThread.handleBindApplication 是 Application 实例创建和初始化的地方
private void ActivityThread.handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// ...
Application app;
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy writesAllowedPolicy = StrictMode.getThreadPolicy();
try {
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
// ...
} ...
}
public Application LoadedApk.makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass, Instrumentation instrumentation) {
// ...
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
// ...
try {
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "initializeJavaContextClassLoader");
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
// ... 创建 Application 实例
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} ...
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app); // 这里会调用生命周期函数 onCreate
} ...
}
return app;
}
public Instrumentation.Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = getFactory(context.getPackageName()).instantiateApplication(cl, className);
app.attach(context); // 在这里会调用 attachBaseContext
return app;
}
// 最终调用 loadClass 加载 app Application 类
Application AppComponentFactory.instantiateApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Application) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}